Anti-Black Racism in Canada and its Effects on Health
Samantha Mannala
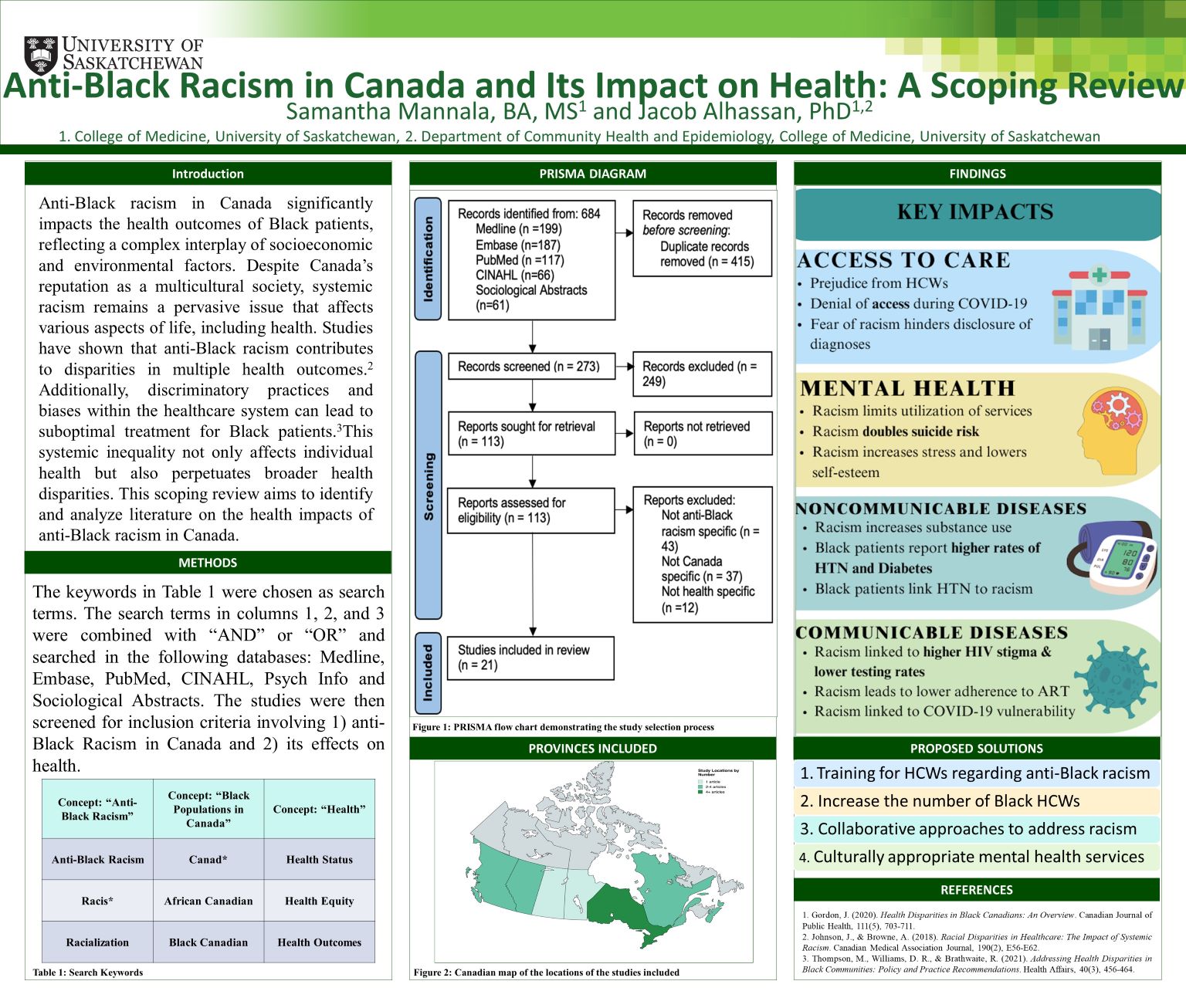
Anti-Black racism in Canada profoundly impacts the health outcomes of Black patients, reflecting a complex interplay of socioeconomic and environmental factors. Despite Canada's reputation as a multicultural society, systemic racism continues to influence various life aspects, including health. This scoping review aims to identify and analyze literature on the health impacts of anti-Black racism in Canada.
Search terms related to anti-Black racism, Black populations in Canada, and health were used to query multiple databases. Studies were screened for inclusion based on their focus on anti-Black racism in Canada and its effects on health, resulting in 21 studies for analysis.
Our review reveals that anti-Black racism adversely impacts Canadian Black patients in four key areas: healthcare access, mental health, noncommunicable diseases, and communicable diseases. Black patients report challenges in accessing healthcare due to prejudice from healthcare workers and denial of services. Additionally, racism contributes to poorer mental health outcomes and exacerbates noncommunicable diseases like hypertension, diabetes, and substance use, as well as communicable diseases such as HIV and COVID-19. Proposed solutions include enhanced training for healthcare workers, increasing the representation of Black healthcare workers, developing culturally appropriate mental health services, and implementing collaborative approaches to combat racism and improve health outcomes.
