The Effect of the COVID-19 Pandemic on Head and Neck Abscess Admissions: A Retrospective Chart Review
Osman Badawi
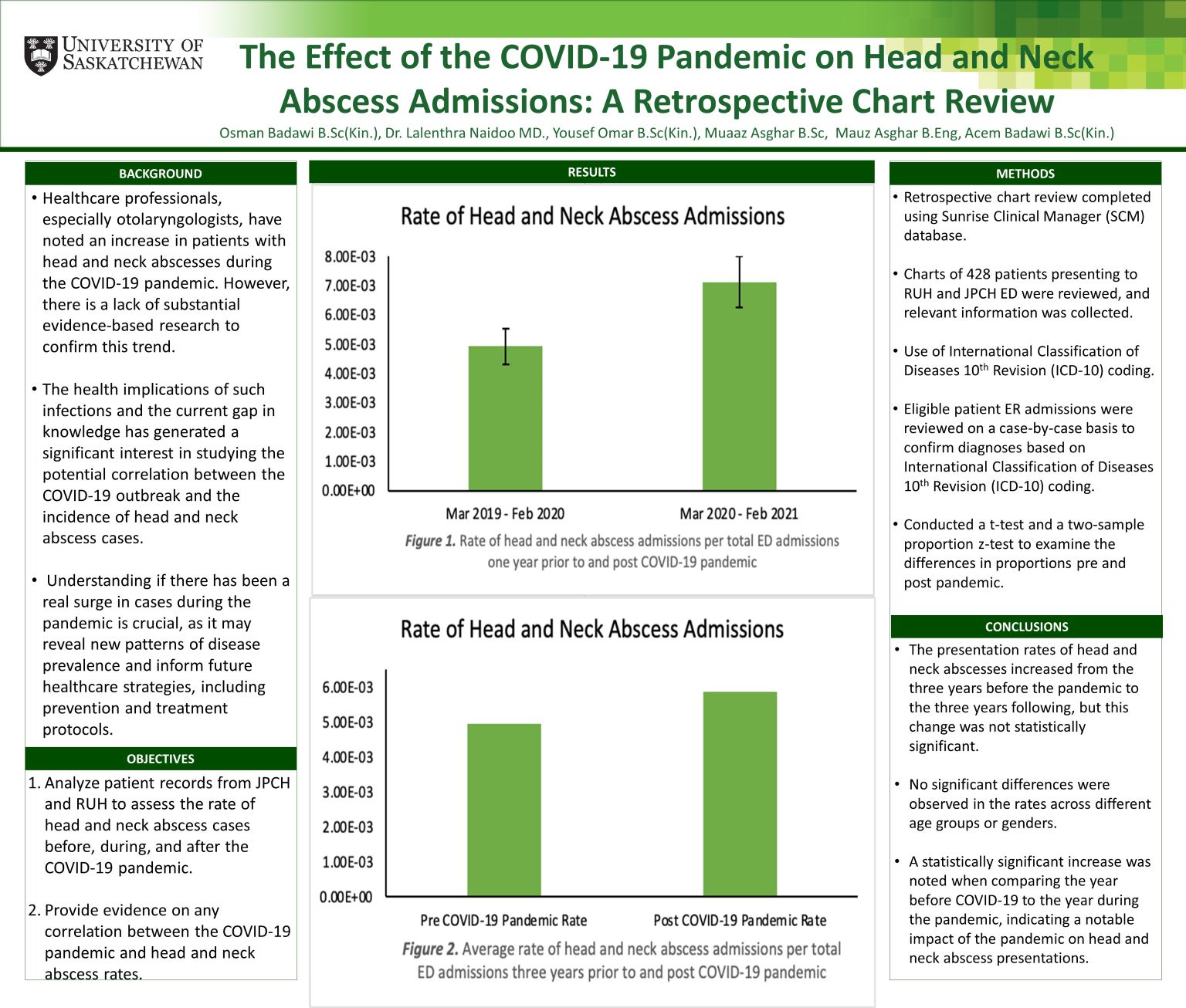
Objective: During the COVID-19 pandemic, otolaryngologists noticed a rise in head and neck abscess cases, though limited research exists on this trend. This study examined whether the pandemic influenced abscess cases by reviewing patient records from Jim Pattison Children’s Hospital (JPCH) and Royal University Hospital (RUH). The goal is to identify changes in prevalence and inform future healthcare strategies.
Methods: A retrospective review of patient charts from March 1, 2017, to February 28, 2023, was conducted using the SCM database. ICD-10 codes identified cases of head and neck abscesses, and data on patient demographics, COVID-19 and vaccination status, diagnosis, treatment, and admission were recorded. Diagnoses were verified via hospital notes. A t-test compared incidence rates before and after the pandemic.
Results: Abscess rates rose from 4.96 E-3 pre-pandemic to 5.86 E-3 post-pandemic, but the increase was not statistically significant. No significant differences were seen across age or gender. The largest difference was between the year before (4.93 E-3) and during the pandemic (7.13 E-3), a statistically significant increase.
